Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kenzhina, I.*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Ho, H. Q.; Sakamoto, Naoki*; Okumura, Keisuke; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Chikhray, Y.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 164, p.112181_1 - 112181_5, 2021/03
Tritium release into the primary coolant during operation of the JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor) and the JRR-3M (Japan Research Reactor-3M) had been studied. It is found that the recoil release by  Li(n
Li(n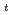 ,
, )
) H reaction, which comes from a chain reaction of beryllium neutron reflectors, is dominant. To prevent tritium recoil release, the surface area of beryllium neutron reflectors needs to be minimum in the core design and/or be shielded with other material. In this paper, as the feasibility study of the tritium recoil barrier for the beryllium neutron reflectors, various materials such as Al, Ti, V, Ni, and Zr were evaluated from the viewpoint of the thickness of barriers, activities after long-term operations, and effects on the reactivities. From the results of evaluations, Al would be a suitable candidate as the tritium recoil barrier for the beryllium neutron reflectors.
H reaction, which comes from a chain reaction of beryllium neutron reflectors, is dominant. To prevent tritium recoil release, the surface area of beryllium neutron reflectors needs to be minimum in the core design and/or be shielded with other material. In this paper, as the feasibility study of the tritium recoil barrier for the beryllium neutron reflectors, various materials such as Al, Ti, V, Ni, and Zr were evaluated from the viewpoint of the thickness of barriers, activities after long-term operations, and effects on the reactivities. From the results of evaluations, Al would be a suitable candidate as the tritium recoil barrier for the beryllium neutron reflectors.
Kenzhina, I.*; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Okumura, Keisuke; Ho, H. Q.; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Chikhray, Y.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(1), p.1 - 8, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The sources and mechanisms for the tritium release into the primary coolant in the JMTR and the JRR-3M containing beryllium reflectors are evaluated. It is found that the recoil release from chain reaction of  Be is dominant and its calculation results agree well with trends derived from the measured variation of tritium concentration in the primary coolant. It also indicates that the simple calculation method used in this study for the tritium recoil release from the beryllium reflectors can be utilized for an estimation of the tritium release into the primary coolant for a research and testing reactors containing beryllium reflectors.
Be is dominant and its calculation results agree well with trends derived from the measured variation of tritium concentration in the primary coolant. It also indicates that the simple calculation method used in this study for the tritium recoil release from the beryllium reflectors can be utilized for an estimation of the tritium release into the primary coolant for a research and testing reactors containing beryllium reflectors.
Okumura, Keisuke; Oki, Shigeo*; Yamamoto, Munenari*; Matsumoto, Hideki*; Ando, Yoshihira*; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Sasahara, Akihiro*; Katakura, Junichi; Matsumura, Tetsuo*; Aoyama, Takafumi*; et al.
JAERI-Research 2004-025, 154 Pages, 2005/01
This report summarizes the activity (FY2000-2003) of Working Group (WG) on Evaluation of Nuclide Generation and Depletion under Subcommittee on Nuclear Fuel Cycle of Japanese Nuclear Data Committee. In the WG, analyses of Post Irradiation Examinations have been carried out for UO and MOX fuels irradiated in PWRs, BWRs and FBRs, and for actinide samples irradiated in fast reactors, by using ORIGEN or more detailed calculation codes with their libraries based on JENDL-3.2, JENDL-3.3 and other foreign nuclear data files. From these results, current prediction accuracy and problems for evaluation of nuclide generation and depletion are discussed. Furthermore, this report covers other products of our activity; development of the ORIGEN libraries for PWR, BWR and FBR based on JENDL-3.3, study on introduction of neutron spectrum index to ORIGEN calculations, and results of questionnaire survey on desirable accuracy of ORIGEN calculations.
and MOX fuels irradiated in PWRs, BWRs and FBRs, and for actinide samples irradiated in fast reactors, by using ORIGEN or more detailed calculation codes with their libraries based on JENDL-3.2, JENDL-3.3 and other foreign nuclear data files. From these results, current prediction accuracy and problems for evaluation of nuclide generation and depletion are discussed. Furthermore, this report covers other products of our activity; development of the ORIGEN libraries for PWR, BWR and FBR based on JENDL-3.3, study on introduction of neutron spectrum index to ORIGEN calculations, and results of questionnaire survey on desirable accuracy of ORIGEN calculations.
Suyama, Kenya; Mochizuki, Hiroki*; Okuno, Hiroshi; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
Proceedings of International Conference on Physics of Fuel Cycles and Advanced Nuclear Systems; Global Developments (PHYSOR 2004) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2004/04
This paper provides validation results of SWAT2, the revised version of SWAT, which is a code system combining point burnup code ORIGEN2 and continuous energy Monte Carlo code MVP, by the analysis of post irradiation examinations (PIEs). Some isotopes show differences of calculation results between SWAT and SWAT2. However, generally, the differences are smaller than the error of PIE analysis that was reported in previous SWAT validation activity, and improved results are obtained for several important fission product nuclides. This study also includes comparison between an assembly and a single pin cell geometry models.
Shibata, Taiju; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Miyamoto, Satoshi*; Ogura, Kazutomo*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 223(2), p.133 - 143, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.87(Nuclear Science & Technology)The High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) can provide very large spaces at high temperatures for irradiation tests. The I-I type irradiation equipment was developed as the first irradiation rig. It will be served for an in-pile creep test on a stainless steel with large standard size specimens. It uses the ambient high temperature of the core for the irradiation temperature control. The target irradiation temperatures are 550 and 600 C with the target temperature deviation of
C with the target temperature deviation of  3
3 C. In this study, the irradiation temperature changes at transient conditions were analyzed by an FEM code and the temperature controllability of the equipment was examined by a mockup test. The controllability was evaluated with the measured temperature transient data at the core graphite components in the Rise-to-Power tests of the HTTR. The result indicates that the temperature control method of the equipment is effective to keep the irradiation temperature stable in the irradiation test.
C. In this study, the irradiation temperature changes at transient conditions were analyzed by an FEM code and the temperature controllability of the equipment was examined by a mockup test. The controllability was evaluated with the measured temperature transient data at the core graphite components in the Rise-to-Power tests of the HTTR. The result indicates that the temperature control method of the equipment is effective to keep the irradiation temperature stable in the irradiation test.
Sasajima, Hideo; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Nakamura, Takehiko; Fuketa, Toyoshi; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 7th International Topical Meeting on Research Reactor Fuel Management (ENS RRFM2003), p.109 - 113, 2003/03
Uranium-zirconium hydride (U-ZrHx) fuel has been widely utilized in the world as TRIGA reactor fuel. In order to obtain the fuel performance data under accident conditions and to enhance accountability of the safety assessment of the reactors using the fuel, irradiation tests under power burst type accident conditions have been conducted in the NSRR. Five pulse irradiation tests have been performed at peak fuel enthalpies ranging from 187 J/g to 483 J/g. Cladding surface temperature increased rapidly at the pulse and DNB occurred in peak fuel enthalpy over 187 J/g in the tests. The DNB occurred at lower fuel enthalpy in the U-ZrH1.6 fuel than in the UO fuel rods. The rod internal pressure rose up to as high as 1MPa in the transient heating tests, suggesting considerable release of the hydrogen decomposed from the fuel. The peak pressure was lower than equilibrium hydrogen pressure of 1.5MPa at the peak temperature, suggesting the transient effect. Considerable PCMI was observed in the tests, through cladding elongation up to 3.3 mm synchronized to the pellet stack deformation.
fuel rods. The rod internal pressure rose up to as high as 1MPa in the transient heating tests, suggesting considerable release of the hydrogen decomposed from the fuel. The peak pressure was lower than equilibrium hydrogen pressure of 1.5MPa at the peak temperature, suggesting the transient effect. Considerable PCMI was observed in the tests, through cladding elongation up to 3.3 mm synchronized to the pellet stack deformation.
Shibata, Taiju; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Shimakawa, Satoshi
Reactor Dosimetry in the 21st Century, p.211 - 218, 2003/00
The High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) is the first HTGR in Japan with a maximum power of 30 MW. The construction of it was completed successfully in March 2002. The HTTR aims to perform irradiation studies at its very wide irradiation spaces at high temperatures. Although the creep behavior of materials is measured by the large standard size specimens at out-of-pile, small size ones are generally used for in-pile creep tests because of the irradiation capability of reactors. The I-I type irradiation equipment, the first rig for the HTTR, is to be used for the in-pile creep test on a stainless steel with the standard specimens. The rig can give big tensile loads of about 9.8 kN on them. The temperatures of 550 and 600 C and the fast neutron fluence of 1.2
C and the fast neutron fluence of 1.2 10
10 n/m
n/m are the targets of the test. Prior to the in-pile creep test, the in-core irradiation properties at the irradiation region are to be obtained by the rig as the first irradiation test. This paper describes the dosimetry plan at the first irradiation test and the subsequent data assessment procedure.
are the targets of the test. Prior to the in-pile creep test, the in-core irradiation properties at the irradiation region are to be obtained by the rig as the first irradiation test. This paper describes the dosimetry plan at the first irradiation test and the subsequent data assessment procedure.
Shibata, Taiju; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Miyamoto, Satoshi*; Ogura, Kazutomo*
JAERI-Tech 2002-097, 19 Pages, 2002/12
The HTTR aims to establish and upgrade the technological basis for the HTGRs and to perform the innovative basic research on high temperature engineering. The HTTR is planned to be used to perform various tests such as, the safety demonstration test, high temperature test operation and irradiation test with large irradiation fields at high temperatures. This paper describes the design of the I-I type irradiation equipment, developed as the first rig for the HTTR, and does the planned dosimetry method at the first irradiation test. It was developed to perform in-pile creep test on a stainless steel with large standard size specimens. It can give great loads on the specimens stably and can control the irradiation temperature precisely. The in-core data are measured by differential transformers, thermocouples, SPNDs and neutron fluence monitors. The obtained data at the first test can be contributed to upgrade the technological basis for the HTGRs, since it is the first direct measurement of the in-core irradiation environments.
Suyama, Kenya; Kiyosumi, Takehide*; Mochizuki, Hiroki*
JAERI-Data/Code 2000-027, 88 Pages, 2000/07
no abstracts in English
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki; Ugajin, Mitsuhiro; *
Kaku Nenryo Kogaku; Genjo To Tembo, p.285 - 304, 1993/11
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 7530, 70 Pages, 1978/02
no abstracts in English
Journal of Chemical Physics, 45(1), p.275 - 282, 1966/00
no abstracts in English